Does Your Child Experience Frequent Dizziness?
A balance disorder is a condition marked by the symptoms of feeling unsteady or dizzy. Even while standing, lying or sitting still, a child with a balance disorder might feel as if they are moving, spinning or floating.
More than 1 in 20 children in the nation experience dizziness or some form of balance disorder. The chances of a child developing such a disorder also increases if they have hearing loss. There are a few warning signs if your child may be experiencing dizziness or balance issues:
- Delayed motor milestones – sitting, crawling, walking
- Abnormal eye movements
- Frequent falls or imbalance
- Motion sickness in a car or from moving objects
- Nausea or vomiting
- Reading difficulties – skipping words, unable to follow along
- Disorganized handwriting
- Difficulty walking in dark places
The pediatric vestibular and balance clinic at the Callier Center for Communication Disorders can evaluate children ages 3 months through 12 years of age for vestibular and balance disorders.
Pediatric Comprehensive Assessment of Balance
Children who fail the pediatric vestibular screening are referred for a comprehensive assessment of balance that includes the following types of diagnostic tests:
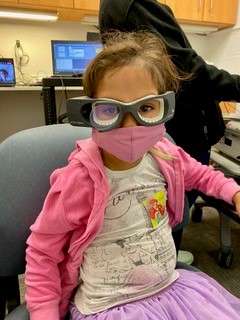
- Videonystagmography (VNG): This series of tests measures eye movements via a pair of video goggles worn by the patient. A VNG consists of three parts: evaluation of eye movements as they follow a visual target, positional tests for measuring dizziness in response to different head and body positions and a caloric test that measures responses to warm and cold air circulating in the ear canal.
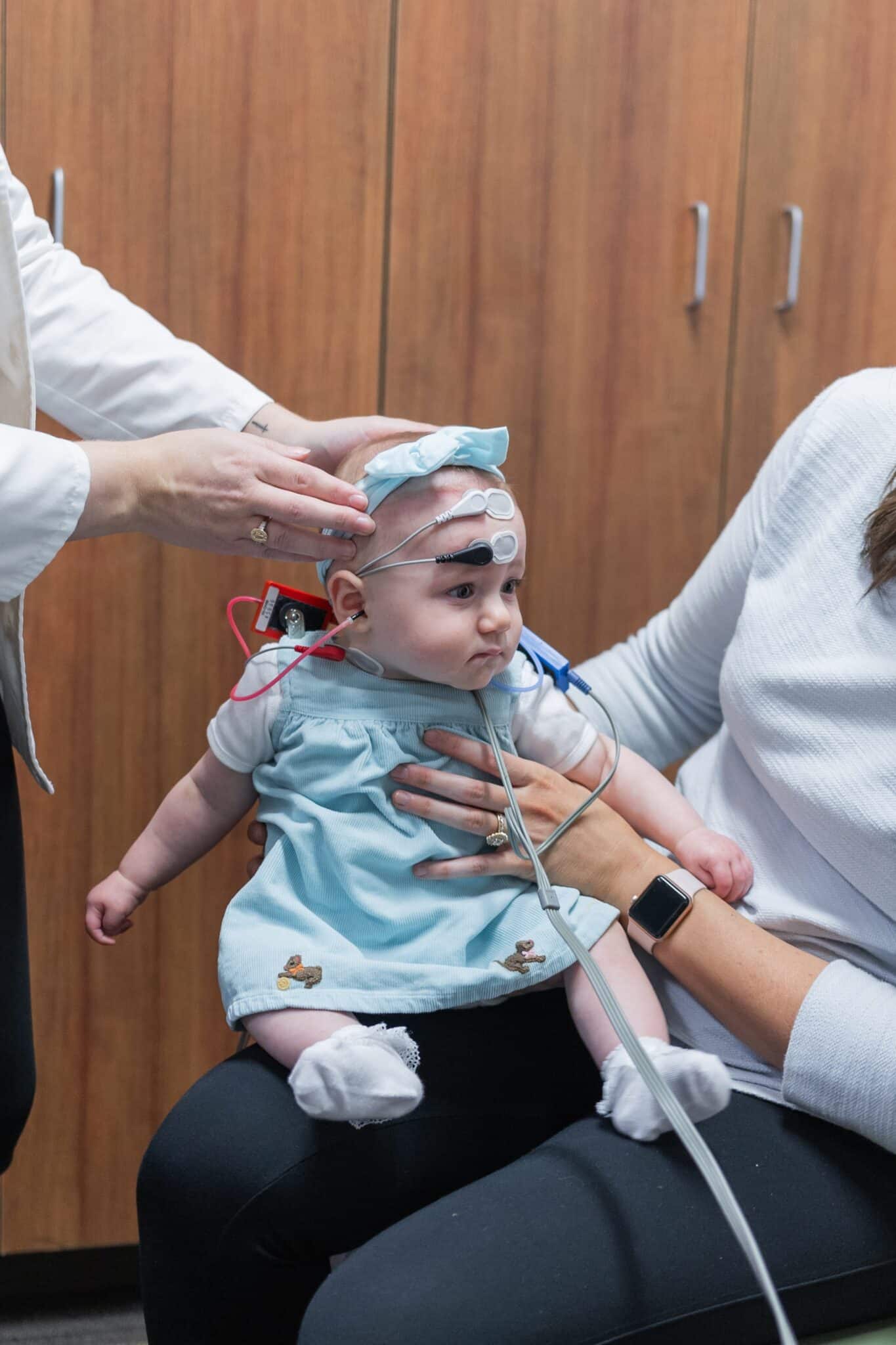
- Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential (VEMP): VEMP testing is used to determine whether the saccule and utricle (inner ear organs) and the vestibular nerve is functioning properly. Electrodes are attached to the neck or under the eyes and sounds are transmitted through a pair of headphones while your child watches a fun video or cartoon.
- Video Head Impulse Test (VHIT): This test is used to measure the eyes’ ability to maintain a steady gaze during head movements. The patient wears video goggles that record the eyes during rapid head movements while your child focuses on stickers or objects on a wall.
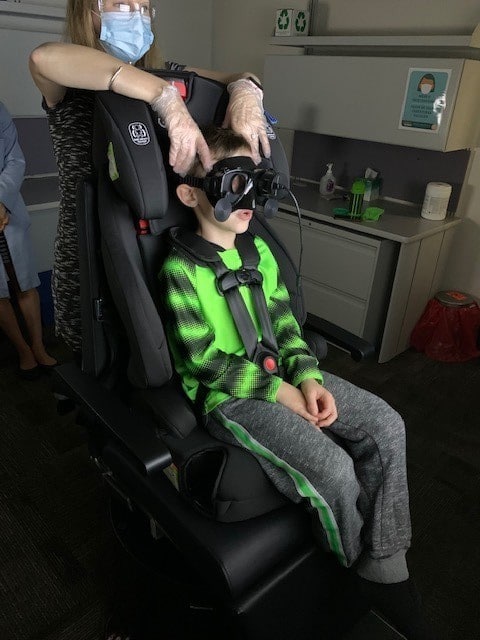
- Rotational Chair Testing: This test includes different sub-tests, which are designed to help determine if your dizziness or imbalance is a result of a vestibular system or central nervous system problem. Your child wears fun goggles while rotating back and forth.
Pediatric Vestibular Screening
The pediatric vestibular screening is a 30-minute appointment that screens children ages 4 to 12 years old for vestibular disorders using basic eye evaluations and the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency, Second Edition (BOT-2), Subtest 5: Balance. This is a fun evaluation that can be completed quickly and will determine if a child is performing according to their age or if they need further evaluation.
You Have Options
Treatment for balance issues take many forms, depending on the cause. Your child’s doctor will try to target the underlying condition in order to reduce or eliminate the symptoms. Treatment options might include:
- Medications (antihistamines, sedatives, antibiotics or steroids)
- Physical or occupational therapy
- Surgery
- Repositioning exercises
- Vestibular retraining programs
- Lifestyle modifications (such as dietary changes)
Our licensed and certified audiologists are trained in the evaluation of pediatric balance and vestibular disorders. Equipped with a comprehensive array of screening and testing tools, we are here to develop a treatment strategy that works for your child’s – and family’s – individual needs.
Early detection is vital in treating vestibular disorders in infants and children. Schedule an appointment at our Pediatric Balance and Vestibular Clinic today!